Lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries are popular choices for energy storage. Both have unique features and uses.
Understanding their differences helps in choosing the right battery for your needs. Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in gadgets and electric vehicles. They are known for high energy density and long lifespan. Sodium-ion batteries are newer, offering cost-effective and environmentally friendly options.
Comparing them can provide insights into their advantages and limitations. This comparison is crucial for consumers and industries looking for sustainable and efficient energy solutions. By exploring these differences, you can make informed decisions about which battery best suits your application. Whether for personal gadgets or large-scale energy storage, knowing the right battery can impact performance and sustainability.
Basics Of Lithium-ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries power our modern world. They are in smartphones, laptops, and electric cars. These batteries are popular for their efficiency and lightweight design.
Structure And Composition
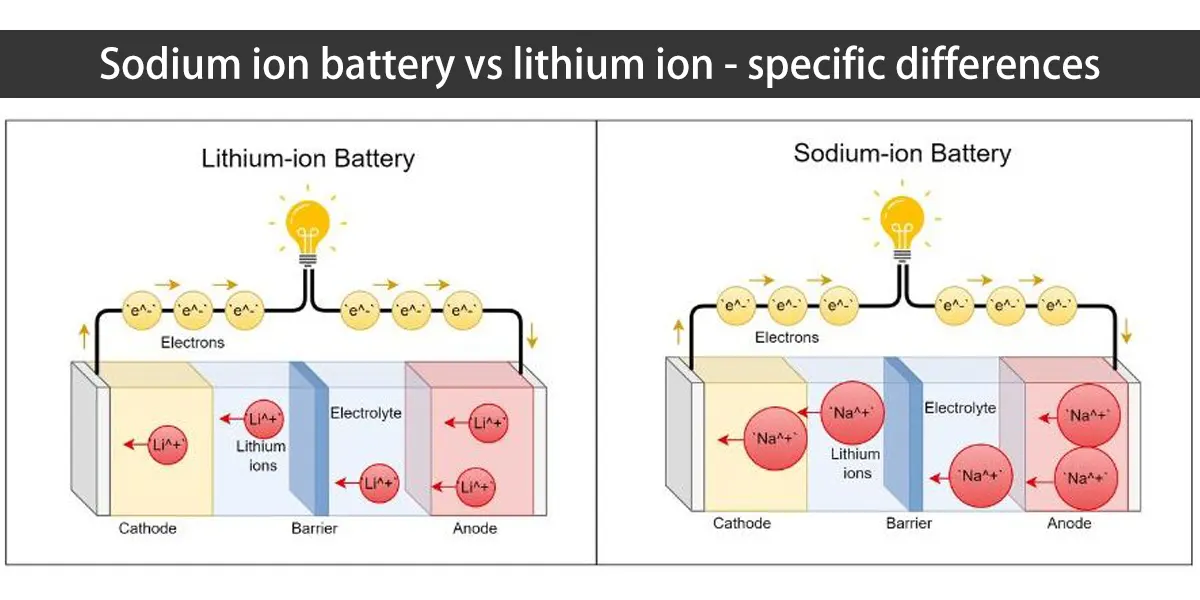
Lithium-ion batteries have several key components. The anode, made of graphite, stores lithium ions. The cathode, often made from lithium cobalt oxide, releases ions. Electrolytes help ions move between the anode and cathode. The separator keeps the anode and cathode apart, preventing short circuits.
Applications And Usage
Lithium-ion batteries are versatile. They power portable electronics like phones and tablets. Electric vehicles rely on them for long-range travel. Renewable energy systems use them to store solar and wind power. Their light weight and high energy density make them ideal for these applications.
Credit: www.huntkeyenergystorage.com
Basics Of Sodium-ion Batteries
Sodium-ion batteries are gaining attention as an alternative to lithium-ion. They offer a sustainable option due to the abundance of sodium. Their potential lies in cost-effectiveness and availability. These batteries share similarities with lithium-ion but have unique features.
Structure And Composition
Sodium-ion batteries consist of an anode, cathode, and electrolyte. The anode often uses hard carbon materials. The cathode typically contains sodium compounds. These elements facilitate the movement of sodium ions. The electrolyte serves as a medium for ion exchange. It ensures efficient energy transfer between electrodes.
Applications And Usage
Sodium-ion batteries are suitable for various applications. They are used in large-scale energy storage systems. Power plants can benefit from their efficiency. These batteries are also considered for electric vehicles. They provide an affordable solution for energy storage. Their use in consumer electronics is still under research.
Performance Comparison
In the world of batteries, performance matters. Lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries compete for attention. Each has strengths and weaknesses. Understanding their performance helps in choosing the right one.
Energy Density
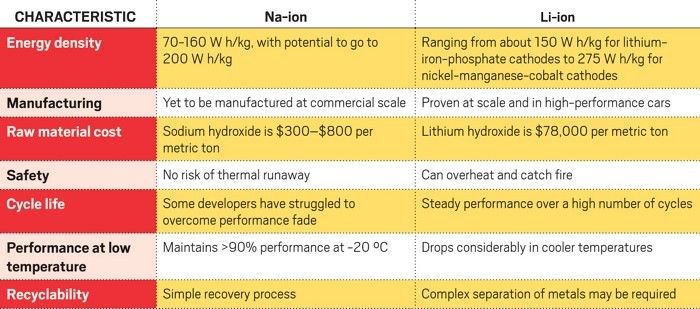
Energy density measures how much energy a battery holds. Lithium-ion batteries have high energy density. This means they store more energy in less space. Devices can be smaller and lighter with lithium-ion batteries. Sodium-ion batteries have lower energy density. They store less energy in the same space. This can lead to larger and heavier devices.
Charging Speed
Charging speed is crucial for daily use. Lithium-ion batteries charge quickly. Fast charging keeps devices ready for use. Sodium-ion batteries charge slower. Users may wait longer for full charge. This affects convenience and usability.
Credit: worldsustainabilitycollective.com
Cost Implications
Lithium-ion batteries often cost more due to expensive materials. Sodium-ion batteries present a cheaper option, using abundant resources. This cost difference impacts their applications in various industries.
When considering the cost implications of lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries, it’s crucial to evaluate how each type impacts both production and market pricing. Understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions, whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a manufacturer, or just curious about sustainable energy options. Let’s dive into the specifics of production costs and market pricing to see where these two battery types stand.Production Costs
Producing lithium-ion batteries involves significant expenses. Lithium extraction is a complex process, often requiring advanced technology and substantial energy input. This can drive up costs, making lithium-ion batteries more expensive to produce. Sodium-ion batteries, on the other hand, utilize sodium, a far more abundant and accessible resource. This can result in lower production costs. If you’re considering the long-term economic impact, sodium-ion could offer a more budget-friendly option. However, sodium-ion technology is still in its developmental stages. Initial production costs could be higher until economies of scale are achieved. This is something to keep in mind if you’re looking at the immediate financial impact.Market Pricing
The market pricing of these batteries reflects their production costs and technological maturity. Lithium-ion batteries currently dominate the market, benefiting from established supply chains and mass production. This can lead to competitive pricing, especially in consumer electronics. But here’s a twist: as sodium-ion technology advances, its market pricing could become more attractive. With lower resource costs and potential for widespread adoption, sodium-ion batteries might offer a cost-effective alternative in the future. If you’re a consumer, this raises an intriguing question: should you invest in the tried-and-true lithium-ion now, or wait for sodium-ion to catch up? Balancing current needs with future possibilities can be a strategic move. In conclusion, the cost implications of choosing between lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries are multifaceted. Consider both production costs and market pricing to make the best decision for your needs. As technology evolves, staying informed will help you navigate these choices effectively.Environmental Impact
Lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries have different environmental impacts. Understanding these impacts can guide sustainable choices in technology.
Resource Availability
Lithium is scarce and concentrated in specific regions. This limits its availability and increases extraction costs. Sodium is abundant and spread globally. This makes it more accessible for battery production.
Recycling And Disposal
Lithium-ion batteries face challenges in recycling. Their complex chemistry requires sophisticated processes. Sodium-ion batteries offer easier recycling options. Their simpler structure allows for more straightforward disposal.
Improving recycling can reduce environmental harm. Efficient disposal methods can minimize waste and pollution.
Safety Considerations
Lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density and lightweight design, but require careful handling due to fire risks. Sodium-ion batteries offer safer alternatives with lower energy density, ideal for less demanding applications, reducing the risk of overheating and explosions.
When it comes to choosing between lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries, understanding safety considerations is crucial. Both types of batteries have their advantages, but safety is a major concern for anyone using them. Whether you’re powering a smartphone or an electric vehicle, knowing the risks can help you make informed decisions. ###Thermal Stability
Lithium-ion batteries are known for their high energy density. However, this advantage comes with a trade-off in thermal stability. If these batteries overheat, they can become unstable and pose a risk. Sodium-ion batteries, on the other hand, offer better thermal stability. They are less prone to overheating, making them a safer option for high-temperature environments. Imagine using a device that never heats up excessively—sounds comforting, right? ###Risk Of Fire And Explosion
One of the biggest concerns with lithium-ion batteries is their potential to catch fire or explode. This usually happens if the battery is damaged or improperly charged. We’ve all heard stories of phones or laptops bursting into flames, which raises eyebrows. Sodium-ion batteries present a lower risk of fire and explosion. Their chemistry is more stable, reducing the chances of catastrophic failure. Would you rather have peace of mind knowing your devices are less likely to turn into a fire hazard? When you weigh the safety considerations, sodium-ion batteries seem to offer a safer profile. But does that make them the better choice for your needs?Technological Advancements
Lithium-ion batteries offer high energy density and longer life, making them ideal for electronics. Sodium-ion batteries, being cheaper and more abundant, suit large-scale energy storage. Both have unique roles in technological progress.
In recent years, the world of battery technology has seen significant breakthroughs, especially with lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries. Both have distinct features that make them suitable for different applications. As technology progresses, understanding these differences can help you make informed decisions about energy storage solutions.Recent Developments
Recent advances in lithium-ion batteries have focused on increasing energy density and reducing costs. Innovations in materials, such as silicon anodes and solid-state electrolytes, have enhanced performance and safety. These advancements make lithium-ion batteries more appealing for consumer electronics and electric vehicles. Sodium-ion batteries, on the other hand, have gained attention due to their abundance and low cost. Research is underway to improve their energy density and cycle life. Companies are experimenting with different cathode materials to make these batteries more competitive in the market.Future Prospects
Looking ahead, lithium-ion batteries are poised to dominate sectors requiring high energy density, like electric vehicles. However, concerns about lithium supply and environmental impact persist. Efforts to recycle and repurpose lithium-ion batteries are expected to grow. Sodium-ion batteries offer a promising alternative, especially for large-scale energy storage. Their potential lies in grid storage and applications where cost is a critical factor. As technology evolves, sodium-ion batteries could become more mainstream, opening new avenues in renewable energy integration. Have you ever considered how these advancements might influence your choice of energy storage? As technology evolves, staying informed can empower you to choose the right solution for your needs.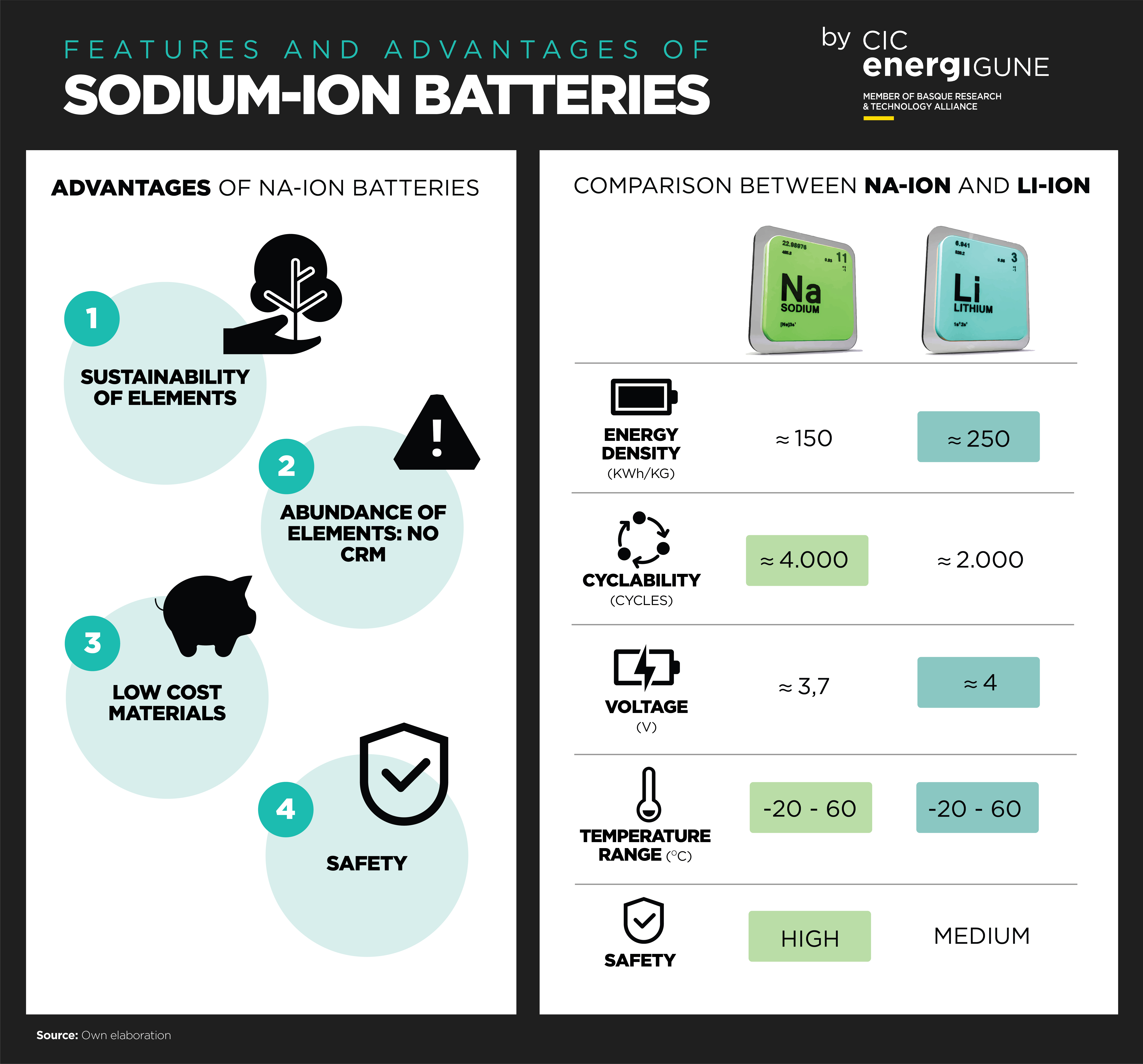
Credit: cicenergigune.com
Market Trends
The energy storage market is evolving rapidly with new technologies. Lithium-ion batteries have dominated for years. Yet, sodium-ion batteries are emerging as a promising alternative. Understanding market trends can help in predicting future growth and adoption. This section explores adoption rates and industry innovations in battery technology.
Adoption Rates
Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in various industries. They power smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles. Their adoption rate is high due to their proven performance. Sodium-ion batteries are gaining attention too. They are seen as a cost-effective choice. Their adoption is slower but growing. Industries are exploring sodium-ion for its abundant resource base.
Industry Innovations
Innovations in lithium-ion technology focus on efficiency. Manufacturers aim to increase energy density. They also work on reducing costs and enhancing safety. Sodium-ion batteries are witnessing innovation too. Research focuses on improving lifespan and performance. New materials are being developed to enhance their capabilities.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Is Better, A Sodium-ion Or A Lithium Ion Battery?
Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer lifespan. Sodium-ion batteries are cheaper and safer. Choose based on your priorities: performance or cost and safety.
Do Sodium-ion Batteries Last Longer Than Lithium-ion Batteries?
Sodium-ion batteries generally have a shorter lifespan than lithium-ion batteries. Lithium-ion batteries offer better energy density and durability. Sodium-ion technology is still developing, and improvements are expected. For now, lithium-ion remains the preferred choice for longevity.
What Are The Disadvantages Of Sodium-ion Batteries?
Sodium-ion batteries have lower energy density than lithium-ion batteries. They are bulkier and heavier, reducing portability. Charge cycles are limited, impacting lifespan. Higher cost and reduced efficiency at low temperatures are major drawbacks. Recycling infrastructure is less developed compared to lithium-ion counterparts.
Why Are Sodium-ion Batteries Not Popular?
Sodium-ion batteries are not popular due to lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries. They are bulkier and heavier. Limited research and development hinder advancements. Production costs remain high. Commercial applications are less developed, reducing market demand.
Conclusion
Choosing between lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries depends on your needs. Lithium-ion batteries offer high energy density and longer life. They are widely used in gadgets like phones and laptops. Sodium-ion batteries are eco-friendly and cheaper. They suit applications where weight isn’t a concern.
Both types have unique benefits. It’s important to consider cost, performance, and environmental impact. Technology continues to evolve, bringing more options. Understanding these differences helps in making informed choices. Whether for personal use or industry, selecting the right battery is crucial.
Make the choice that fits your requirements best.
